
Two common methods of non-invasive CO2 monitoring are.
#ENTITLED CO2 DRIVERS#
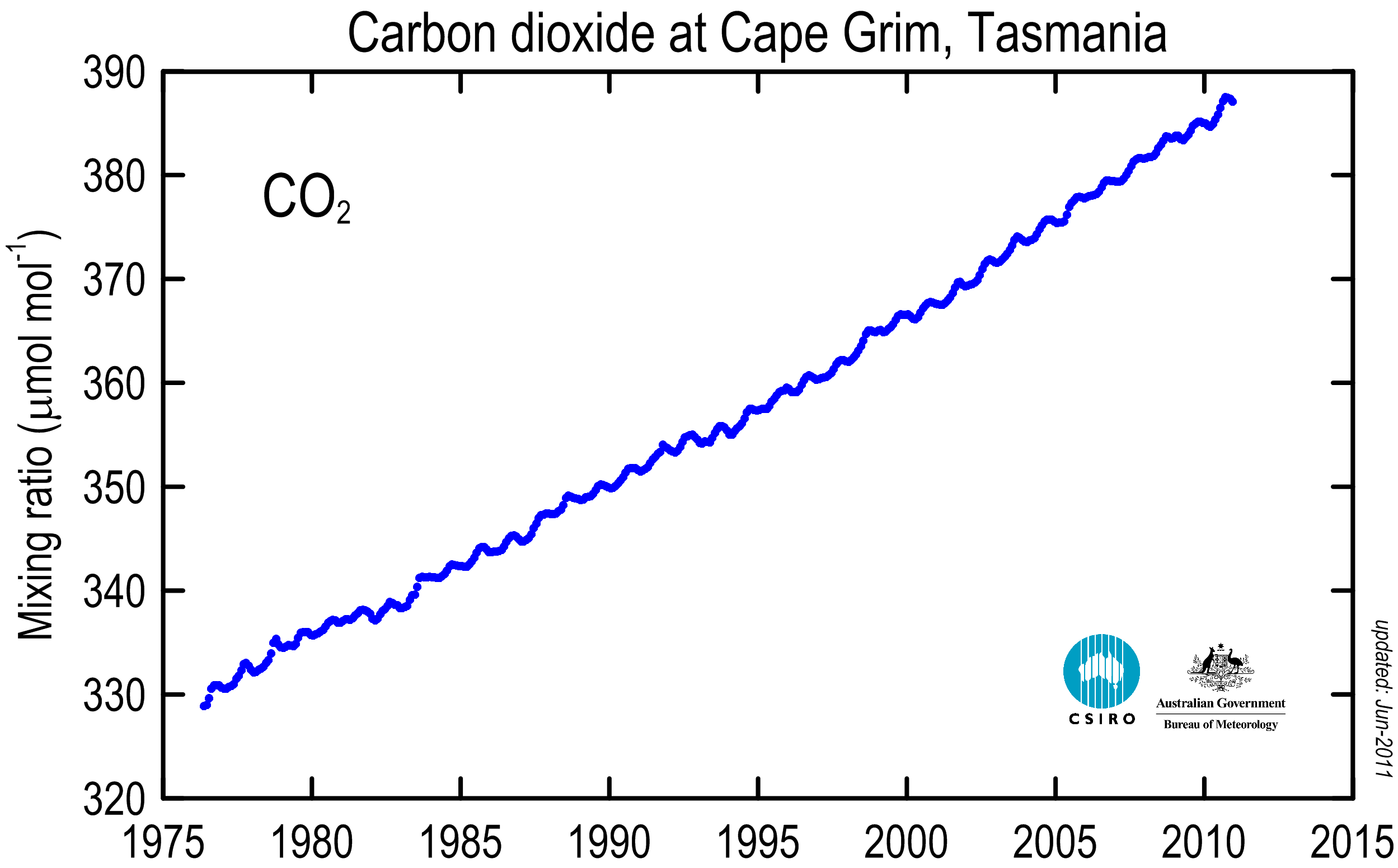
The main drivers for the CADTH Health Technology Assessment report were the growing utility of ETCO 2 monitoring technology in diverse clinical settings, uncertainty in the benefits and cost-effectiveness of capnography devices, and access and implementation issues. Non-invasive carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring has become ubiquitous in anesthesia and critical care and is being increasingly used in neonates. More recently, advances in capnography have expanded its use beyond anesthesiology. A normal curve on capnogram suggests normal CO2 production, adequate circulation, and adequate ventilation. Anesthesiologists have been using capnography for decades to monitor ETCO 2 in patients receiving general anesthesia. Capnography devices have application across several hospital and pre-hospital settings the technology is at various stages of adoption, depending on the clinical area. With capnography, a patient’s ventilation status is monitored in real-time. Capnography is a non-invasive method for ETCO 2 measurement that displays the measurement in both graphical and numerical forms.
The evidence suggests that ETCO 2 measurement can provide an indication of cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow. In fact, it’s commonly called the ventilation vital sign. Aim: End-tidal CO 2 (Et CO2) is the standard in operative care along with pulse oximetry for ventilation assessment. To obtain end-tidal CO2 measurements, CapnoScan requires the animal be intubated and. Also called capnometry or capnography, this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. CapnoScan provides real-time capnography and sidestream sampling. Distal end-tidal CO 2 measured via a double-lumen endotracheal tube was found to have good correlation and agreement with Pa co 2, remained reliable in conditions of severe lung disease, and was more accurate than the standard mainstream proximal end-tidal CO 2.End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO 2) is the level of CO 2 that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETco 2) monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance (ventilation). A subanalysis for infants who weighed <1500 g (13 infants, 84 observations) revealed a good correlation and agreement between distal end-tidal CO 2 and Pa co 2 and poor correlation and agreement for proximal end-tidal CO 2.ĬONCLUSIONS. End-tidal capnography (end-tidal CO2, PETCO2, ET CO2) refers to the graphical measurement of carbon dioxide partial pressure (mm Hg) during expiration.
The accuracy of distal end-tidal CO 2 decreased, but it remained a useful measure of Pa co 2 in the high range of Pa co 2 (≥60 mmHg) or in conditions of severe lung disease. Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide ( CO 2) in the respiratory gases. Distal compared with proximal end-tidal CO 2 had a better correlation with Pa co 2 and a better agreement with Pa co 2. We used for analysis 222 and 212 measurements of distal end-tidal CO 2 and proximal end-tidal CO 2, respectively. Twenty-seven infants (median birth-weight: 1835 g gestational age: 32.5 weeks) participated in the study. Mainstream proximal end-tidal CO 2 was measured via capnograph connected to the endotracheal tube. Sidestream distal end-tidal CO 2 was measured by a Microstream capnograph via the extra port of a double-lumen endotracheal tube.

Data were collected prospectively from 2 capnographs simultaneously and compared with Pa co 2. Included in the study were all infants who were ventilated with conventional mechanical ventilation and intubated with a double-lumen endotracheal tube in our NICU during the study period. The objective of this study was to evaluate a novel method of distal end-tidal CO 2 capnography by comparison with Pa co 2 and with the more standard method that measures mainstream proximal end-tidal CO 2 in intubated infants.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
